Why Did
Theater Become
Important to
Life in Ancient
Greece?

Theater first became established in Greece in what was then the city-state of Athens, shortly before what we know as the classical period of Ancient Greece.

Lord Dionysus
The authorities held annual festivals to honor the god Dionysus to promote peace and community between individuals and neighboring city-states following the 480BC Great Destruction of Athens.
The first shows were often individual poets acting out their written works. These shows quickly started to attract large audiences, which subsequently led to the production of longer scripts and people specifically choosing to act out certain roles. It wasn’t long before these shows had writers, directors, and a cast of actors.


Thespis
“The Father of Tragedy”
Shows would also take the form of competitions for who could create the best performance. The earliest recorded competition winner was Thespis, who became known as “The Father of Tragedy.” Thespis is also regarded as one of the founding fathers of drama, which is why we sometimes refer to modern actors as thespians.
Another cornerstone of these festivals were performances of the work of Homer, who lived sometime between the 12th and 8th centuries BC. Around the start of the classical period of Ancient Greece, scholars at the time were beginning to chronicle Homer’s works. Their readings at these shows would be the first stage of bringing Homer into the public consciousness, and he remains revered today.
During this time, playwrights began to pioneer the three main genres of theater

Tragedy

Comedy

Satire
The entire civilization went through a “Golden Age”
It wasn’t just drama and the theater that took off as Ancient Greece entered its classical period. The entire civilization went through a “Golden Age,” where the people were passionate about advancing and creating art, architecture, literature, monuments, philosophy, and drama. You will recognize these as many of the foundations of modern culture. It’s easy to see why many consider Ancient Greece the birthplace of modern civilization!



The Early Days
of Greek Drama
and Theater

Many of the plot devices and other writing tools used by Ancient Greek playwrights still apply and can be seen in modern works. Although we may not know the specifics of what happened during each performance, the dramas of Ancient Greece have stood the test of time.


The popular communication methods of the time were mostly responsible for the rise of early theater.
Verbal communication was of higher value than writing. You couldn’t change the written word. A story had been committed to paper, and that was the story the reader would tell. In contrast, if you spoke, you could take ideas from others or invite them to tell the story alongside you. Collaborative oral storytelling was part of Ancient Greek culture and society for centuries before the establishment of theatrical performance.
When it came to the theater, if the audience thought the actors were not doing a good enough job, they would toss old food or even rocks at them! This theater tradition persisted for many years and would continue into the 20th century in some places!

Early Genre
Development &
The Three Genres

Three genres came to characterize Ancient Greek theater: tragedy, comedy, and satire. Alongside drama and musical, these genres remain popular today and were very much the building blocks of modern theater.
How did each of these genres emerge and develop in Ancient Greece?

The Emergence of the
Tragedy Genre
Early plays were typically tragedies, hence the cultural use of the term “Greek Tragedy” that is still widely used today.
Tragedies were popular because they were the most in-demand stories at the time. Audiences wanted to see a story that ended with a tragedy or that had a tragic moral. Some of Aristotle’s writings indicate dithyrambs inspired many theatrical tragedy productions. Dithyrambs were choral hymns sung in honor of Dionysus at each year’s festival.

Tragedies were also often played out alongside annual rituals undertaken by the Ancient Greeks to honor Dionysus. Citizens would wear masks and sacrifice animals, usually goats while singing dithyrambs or performing a tragic poem or play. This link led to the adoption of Dionysus as the god of the theater, in addition to the other things for which the Ancient Greeks worshipped him.
The first performances of tragedies would only have one actor on stage at a time. Typically, they would perform wearing a mask and full-body costume. The audience would believe them to be delivering “the voices of the Gods.” As such, tragedies that re-enacted a specific god’s life, not always Dionysis, would also become popular.
Later, up to two actors would join performances. However, for many years three was the maximum number of speaking roles allowed in a performance.
One quirky feature of Ancient Greek tragedies is that they always killed their characters off stage so the audience would only hear their implied death. It was seen as inappropriate for death to be shown directly within a scene, even if it enhanced overall performance.


The Emergence of Comedy &
The Three Periods of Comedy
Comedies represented ancient Greek’s daily lives and the absurdities that could happen to them. In contrast, tragedies often were set in the past and were more likely to include appearances from the gods.

Comedy consists of characters who are there solely for the audience to laugh at.
– Aristotle
Aristophanes is credited with writing most of Ancient Greece’s first comedy plays. In Aristotle’s writings around the emergence of the genre, he explains comedy consists of characters who are there solely for the audience to laugh at. They make a mistake, and the audience does not feel pain from seeing it, representing the opposite of tragedy. At the time, comedy was a means of offering an alternative to tragic stories and performances.
Scholars that assess the early comedies of Ancient Greek theater believe they allow us to gain valuable insight into how Ancient Greek society was. Comedy offered a window into the legal system, education, religious practices, and political systems of Ancient Greece. Above all, it allows us to discover what the Ancient Greeks found funny!
Analysis of Ancient Greek pottery designs suggests that actors have been wearing costumes and doing silly actions on stage for thousands of years.
Archilochus and Hipponax’s poems contain sexual humor, which might have been an influence on early Greek comedy.
Dionysus was as much the inspiration for comedy as he was for tragedy. Many songs sung in his honor would include sexual and phallic imagery references, which would become a regular feature in comedies.

We can split the development of comedy in Ancient Greece and specifically Athens into three periods: The Old Comedy, Middle Comedy, and New Comedy periods.
Old Comedy
Saw the actors rely heavily on audience interaction, particularly when singing the popular songs of the time.
Middle Comedy
Saw a reduction in interaction between the actors and the audience. At this time, comedy also developed to become more general in terms of the situation being funny, rather than humor and shame being explicitly directed at the character – or sometimes the actor!
New Comedy
Was the Ancient Greek equivalent of a modern sitcom. Writers introduced narratives to frame stories for audiences beyond what they saw acted out on stage. Elements like prologues were also used to set the scene so that an audience would get a story but with only part of it told through performance. Aspects of strong emotions such as love and hatred were used in a comedic setting for the first time.

The Development of Satire
Satire emerged from tragedy and quickly became popular. Ancient Greek satire was a mix of comedy and drama, sometimes referred to as a tragicomedy. Ancient Greek satire would rely heavily on sexual themes and topics such as drunkenness and is meant to get a lot of laughs from the audience.

Writers designed the characters’ actions to shame people into change by seeing the actors mocked for things they do themselves. These were the main difference between satire and comedy in ancient Greece. Comedy was to be light-hearted, while satire used laughter paired with shame to provide social commentary and to make people or society change.

How Was
Ancient Greek
Theater Funded?

There were many restrictions in place to keep the quality of the plays high. For example, only three actors ever got speaking parts to ensure that everyone accurately memorized their lines. This set up also meant the audience could easily distinguish between the actors. It also helped to keep the competitive festivals balanced.
However, the costs would have been too high for the state to handle on its own. They enlisted wealthy citizens to fund production costs, and they were afforded enormous amounts of respect as a consequence.
Production costs funded by
Wealthy citizens of Greek
Known as choregos & Getting respect
Oversaw the costumes, musicians, rehearsals, and choir singers
They became known as “choregos” and oversaw the costumes, musicians, rehearsals, and choir singers. At the same time, the state paid for professional actors to attend and take part.

The
Architecture
and Acoustics of
Ancient Greek
Theaters

Ancient Greece was home to some of the best architects of the time. They were continually learning and developing their buildings. The theaters of Ancient Greece are a marvel to behold. Their remains are among the most popular tourist attractions in the country to this day. It’s also easy to see where these theaters had a significant impact on the design of today’s venues.
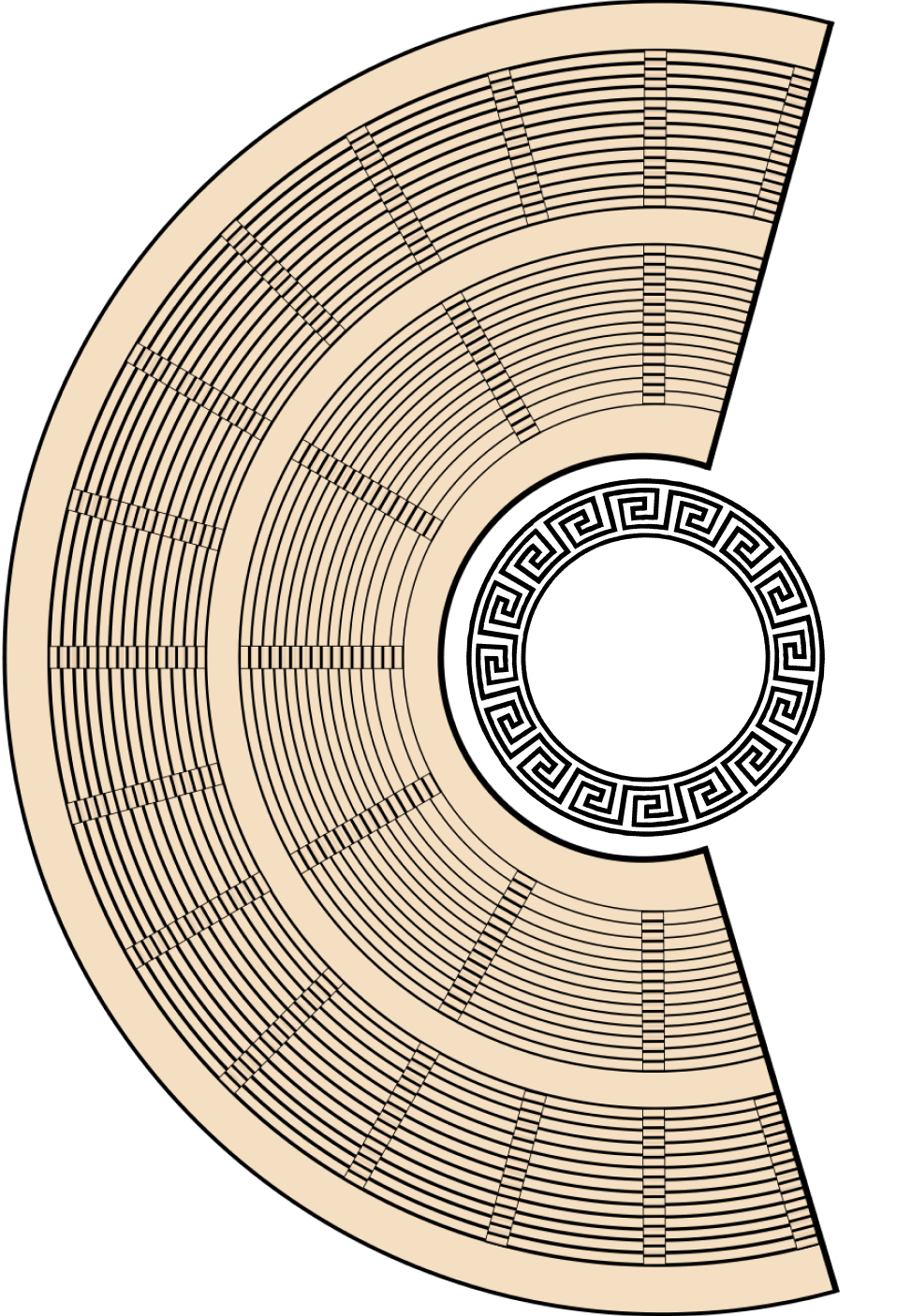
Open-air Theaters
Many of Greece’s cities were built on hills, meaning the seating for theaters could be built into the natural slope. They also were often outside, giving them the name “open-air theaters.” The seating all pointed down towards the stage or the “theatron” as it was called at the time.
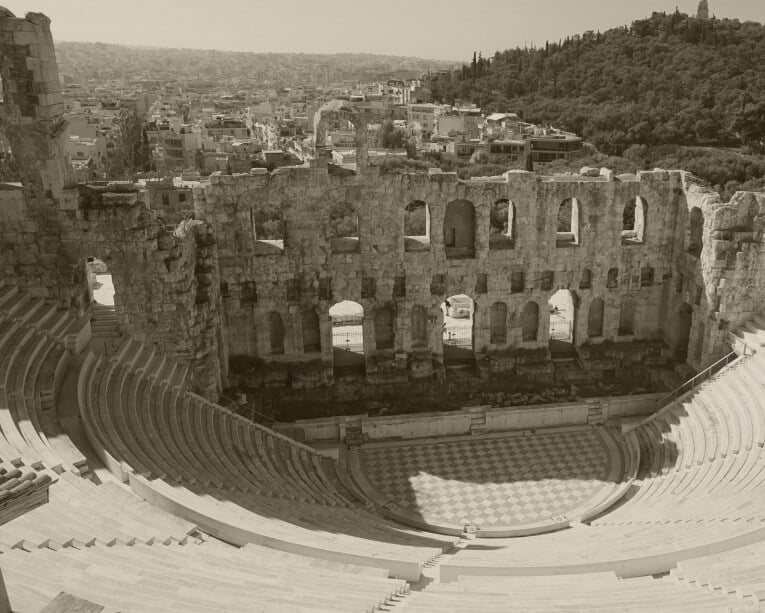

Orchestra & Singing
The theaters’ design also left space for an orchestra or choir in front of the theatron, so music and singing could accompany the actors.
skene
Some theaters included a wall, called a “skene,” which could be decorated or used as a backdrop and gave actors an out of sight area to change their costumes. The word “skene” would lead to the adoption of the term “scene” in later theater, as well as in TV and film.
Research into acoustics by the Ancient Greeks was vast. Such was their work in the fields of architecture and acoustics that we still use their learnings when building new theater venues today.

Gershwin Theater
“The biggest theater on Broadway”
Theaters needed to be significant in size, and able to hold up to 15,000 people at once. In contrast, the biggest theater on Broadway, the Gershwin Theater, only has 1,933 seats!
To ensure everyone at the theater could hear the performance, a lot of time was spent on theaters’ design.

The Tradition of
Masks in
Ancient Greek
Theater

Without the masks, the audience could not hear the actors as well, and those at the top of the theater could not make out the actors’ facial expressions. This meant much of the impact of the play would be lost. These circumstances saw masks quickly establish themselves as an art form and a necessity within the theater.
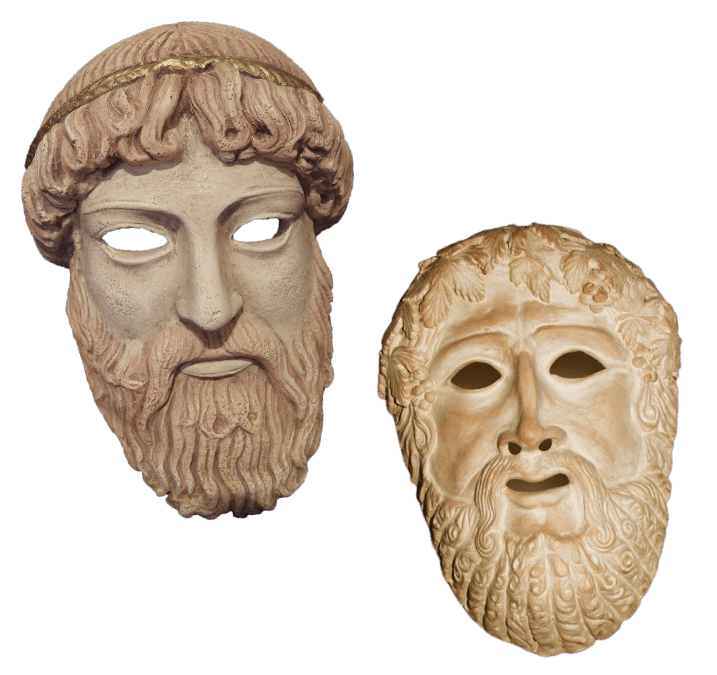

While there are no known examples of Ancient Greek theater masks today, paintings on vases from the 3rd century BC show various actors preparing for their plays and donning masks.
It is also thought masks were left at the altar of Dionysus, or the scene of performances during annual festivals, as an offering to Dionysus.
The actors in a play were often not the only ones wearing masks. It was typical for the choir and orchestra to wear masks to fit the aesthetics of the scene. In a clever twist, while the main actors’ masks would change to express a range of emotions, all choir members would wear matching masks, and wear the same mask throughout, implying they were collectively one character in the show.
Background of the Two Masks
The smiling and crying mask image that we often associate with acting and theater originated during this time. The happy mask was associated with comedy, while the crying mask was associated with tragedies.
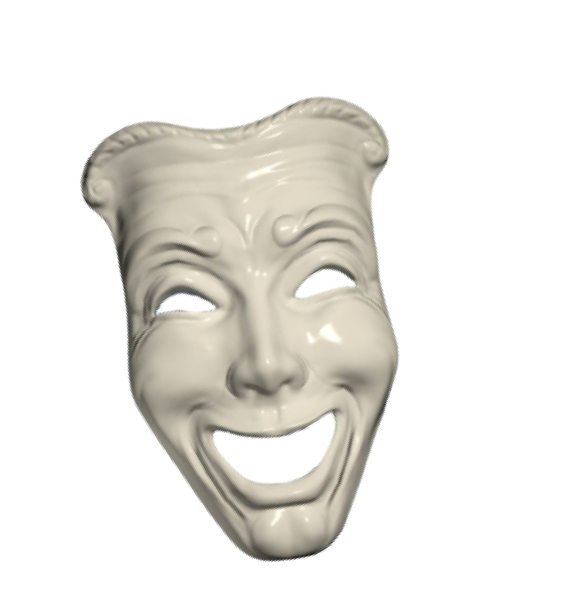

Thalia
“The Muse of Comedy”
The two masks also were a nod to the muses of Greek mythology. Thalia, the Muse of Comedy, was depicted as a cheerful mask. She was young, full of energy, and always smiling. Many statues representing Thalia also include trumpets or other types of horns. Such imagery alludes to how these instruments were used to make an actor’s voice carry in an ancient Greek comedy.
Melpomene
“The Muse of Tragedy”
On the other hand, Melpomene was the Muse of Tragedy. Her mask is sad, and she is often depicted with a weapon in her hand. Sometimes, she even holds the mask itself. Melpomene in art is also seen to be wearing the cothurnus, also known as buskins, which were boots only to be worn by actors performing in tragedies. She also wears a wreath made from a grapevine on her head, which derives from Dionysus.
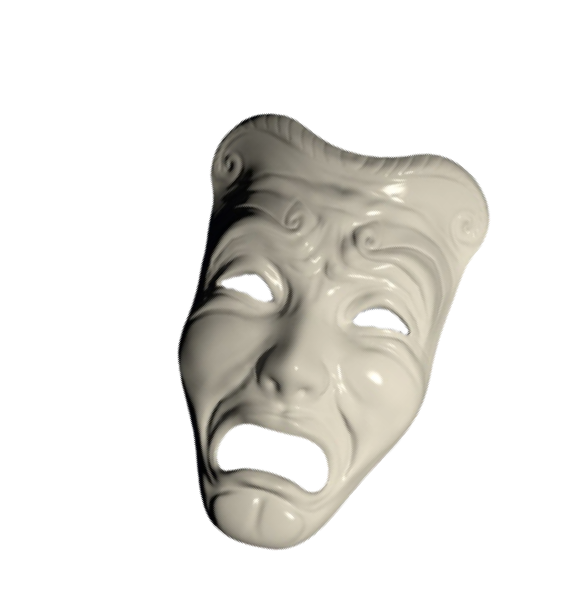

The difference between the two Muses was highly exaggerated and helped showcase the difference between comedy and tragedy.
How Masks were Made
Masks were typically made from natural materials, such as cork, then stiffened up with plaster to hold their shape.
Costumes also typically featured a wig made from animal or human hair, to help keep the actor’s character recognizable. This feature was particularly helpful to audience members who were sat far away from the stage.
During comedies, actors wore bright, cheerful colors and masks. The opposite is true for tragedies, where the characters wore sorrowful and dark colors.

Ancient Greek
Actors

All actors on the stage in a play in Ancient Greece were men, as women were forbidden from performing. Ancient Greeks believed it would be “dangerous” if a woman made her way onto the stage during a performance.
However, that’s not to say female characters did not feature in Ancient Greek plays!
Male actors used intelligent costume design to make themselves appear more feminine when playing a woman character. Costume tweaks included wearing wooden chest plates to create the appearance of having breasts or wearing white stockings. Hence, they looked more feminine at a distance.
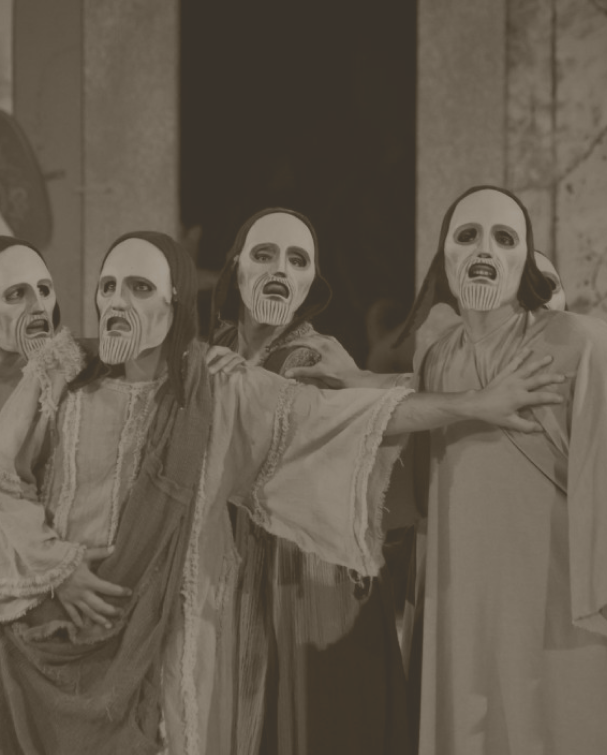


When plays first started being performed professionally, actors lived modestly and were not widely recognized. Society deemed actors as people that poets chose to carry out their works on stage and as nothing more. However, as time went on, recognition and respect for actors quickly grew.
As such, there would soon be demand for certain actors’ shows, and admission prices would subsequently reflect this, too.

Who Went to the
Theater in
Ancient Greece?

While women were not allowed to perform, they were allowed to attend in the audience.
Going to the theater was considered an essential part of Ancient Greek culture, so much so that the government would pay for the poor to attend shows. Since they were giving those who could usually not afford it the money to attend, the government expected every person in Athens to visit a show regularly.
However, there were still divides present at the theater, and it was apparent who belonged to what social class.

The Growth of
Theater Across
Europe and North
Africa

New plays were regularly written and reworked in the theater. Actor’s guilds soon formed and allowed actors to travel and perform. Inspiration from Ancient Greece’s dramas quickly spread across the Mediterranean to southern Europe and North Africa.
Pantomime: a new performance genre
In Rome, Greek plays were translated and produced in Latin. This would eventually lead to the development of pantomime as a new performance genre. As the influence of Ancient Greece on civilization began to decline in the face of other emerging cultures and ideas, Rome would combine pantomime and elements of New Comedy to develop popular dramas that would remain popular through to the establishment of the Roman Empire and beyond.


How Ancient
Greek Theater
Influenced
William
Shakespeare


William
Shakespeare
William Shakespeare is known to have been heavily influenced by the tragedies and comedies of Ancient Greece. Given the influence Shakespeare would later have on modern theater, with his plays being the most popular performances throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, he is perhaps the primary link between Ancient Greek drama and today’s theater.
Shakespeare’s “Hamlet” draws many parallels to the ancient Greek play “Orestes.”
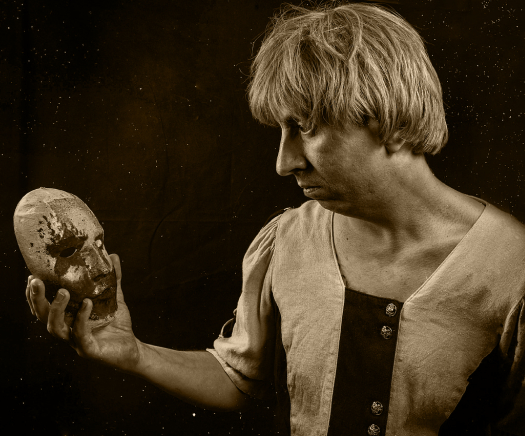

Hamlet
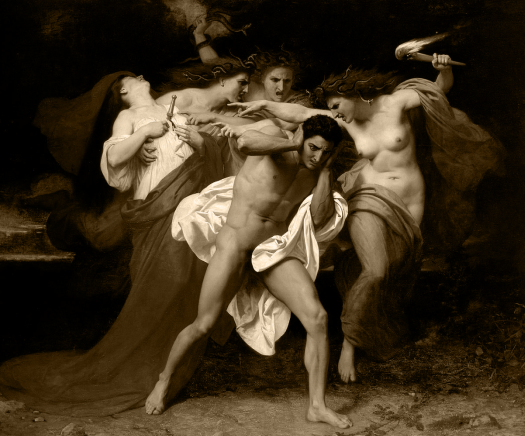

Orestes
In both plays
- A close relative murders the king.
- The main characters are unable to inherit the throne.
- They briefly snap due to stress and guilt.
- They then take their revenge against the new king and their mothers who had married them.
Although the endings of these plays use different mechanisms, it’s clear how Ancient Greek drama influenced Shakespeare. Shakespeare is also known to have studied the tragedies and other plays of Ancient Rome, themselves, of course, evolving from what the Greeks exported across the Mediterranean.

Does Shakespeare’s Influence Today Continue the Legacy of Greek Drama?

Shakespeare’s connection to and influence over contemporary theater is well established. His plays changed a lot of the theater scene, even affecting how storylines and plots evolve within a tale.
Shakespeare’s unique use of the English language is still relevant since he created thousands of words still used today and came up with the idea of using nouns as verbs and verbs as adjectives.

Ancient Greek Dramas’ Influence on Modern Pop Culture

As well as Shakespeare’s widely appreciated influence, there are many references to Greek mythology in the pop culture of today.
Greek myths and stories have been adapted into books, TV shows, video games, and movies, and continue to inspire a variety of creative works today.

Many of these aspects of Ancient Greek life and history were only able to find their way into modern consciousness thanks to drama and the theater.
Remember, Ancient Greek society at the time preferred word of mouth stories. In many cases, the rise in popularity of theatrical productions was the first time stories were documented and preserved. Of course, many of these have evolved into different versions as we understand them today.
Ancient Greece is a part of our everyday lives in the brands we shop with and wear. Have you ever been to a Pandora store or worn a pair of Nike sneakers?

Look up the inspiration behind their brand names after you’ve finished reading this! Many examples of preserved medieval art capture events and stories commonly associated with Ancient Greek dramas. At the same time, even contemporary artists remain inspired by this era.

Ancient Greek Drama and the Theater

Ancient Greece is widely considered one of the cradles of modern civilization and is often thought of as the birthplace of modern society and culture.
From the early days of storytelling to the first performances honoring Dionysus, we can see how theater grew from its Ancient Greek roots into today’s cultural powerhouse.
Elements such as masks, costume, and music are, of course, aspects of performance that we widely associate with modern theatrical shows. In many cases, we wouldn’t consider something a show if it didn’t have these things!



It is impossible to dispute the influence and pathway created by Ancient Greek theater. Whether it’s on Broadway, in London’s West End, or elsewhere, today’s performance art continues to blaze a trail while working with the building blocks established in Athens nearly 3,000 years ago.