The History of
Furniture
Furniture is a part of our everyday lives, from sitting in a cafe, using a table, to sleeping in a bed every night. But how did we get to where we are today?
Although there are modern advancements in the furniture we currently use, furniture has been a part of our history for centuries. Aside from the obvious comfort and practicality furniture provides, it has also been a way to reflect social, cultural, and economic developments throughout history.
When we consider the stone benches found in prehistoric times versus the intricately designed contemporary furniture we use today, it’s clear that furniture design has significantly evolved.
From technological advancements to new materials and societal changes that go hand in hand with artistic movements, many factors have caused furniture evolution to reach its point today.

One thing that has stayed the same throughout furniture’s evolution is the creativity of humans,
with societal changes and technical advancements only bringing more light and possibilities to the budding designers of the world. This article will consider furniture’s broad history, exploring the relationship between social, artistic, and cultural factors with historical and contemporary designs.
Furniture in
Ancient Times

Prehistoric
Furniture
Prehistoric furniture refers to furniture pieces that date back to the earliest times known to humans. At this stage, furniture wasn’t about the aesthetic value or showing off design skills but for practical uses such as sleeping, storing, and sitting. Materials were incredibly limited at this time, with stone, wood, and animal hides being the primary sources for crafting furniture.

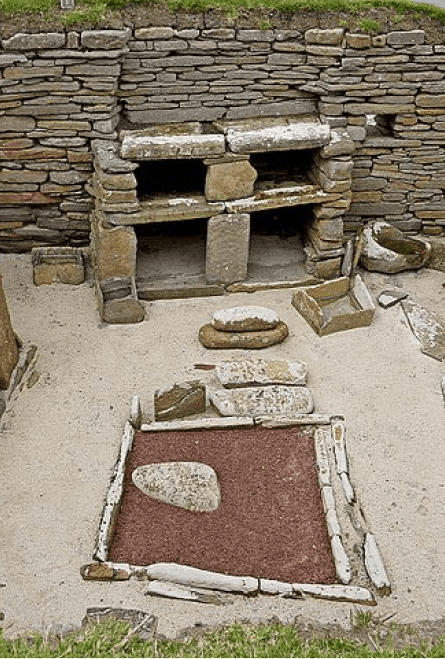
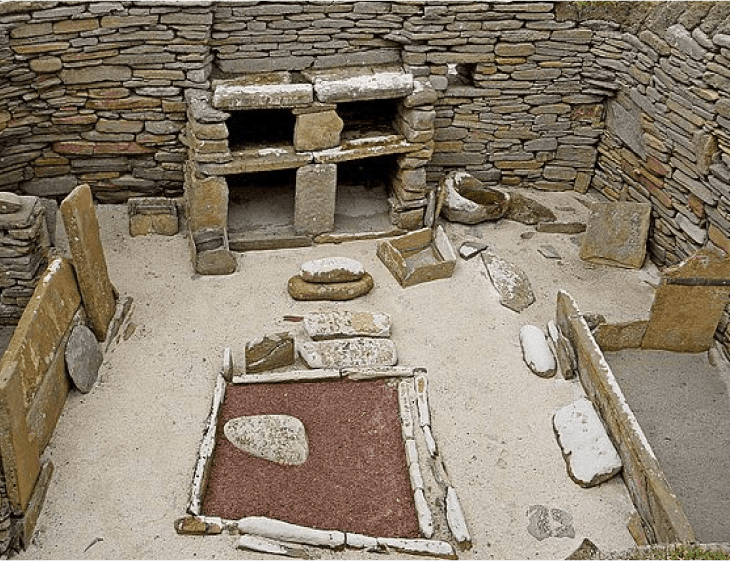
Skara Brae
One of the best preserved Neolithic settlements anywhere in Western Europe
One of the oldest examples of furniture is the Skara Brae settlement, which the Scottish village, Orkney, has preserved.
First discovered in 1820, this village dates back to 3100 BC and shows that villagers used stone to make drawers, beds, and dressers.
For comfort, beds were covered with animal hides and filled with straw, softening the hardness of the stone while providing warmth.

Furniture was also an integral part of both Ancient Egyptian and Greek culture, in which wood was the primary material used, with stone lent to more dramatic furniture, such as thrones and ceremonial pieces.
While prehistoric furniture lacked the style and intricateness of modern-day furniture, these early designs are the reason that we have practical furniture today and were pivotal in the evolution of design and production.
Ancient Egyptian
Furniture
In Ancient Egypt, furniture began to evolve from only being used for practicality and instead saw societal change alter how furniture was viewed. For example, high-quality furniture could indicate your wealth and social status, used as an important status symbol.
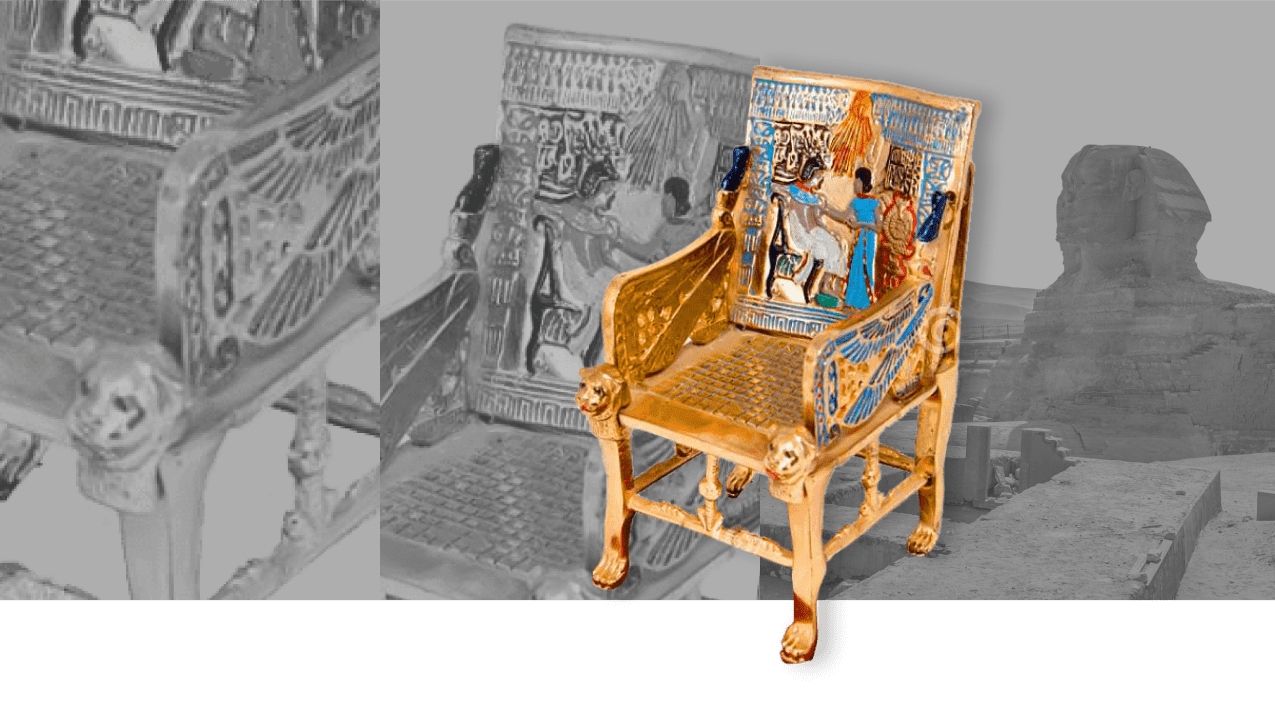
Ancient Egyptians are famous for their skilled woodwork, with many historical designs that have been preserved, indicating this.
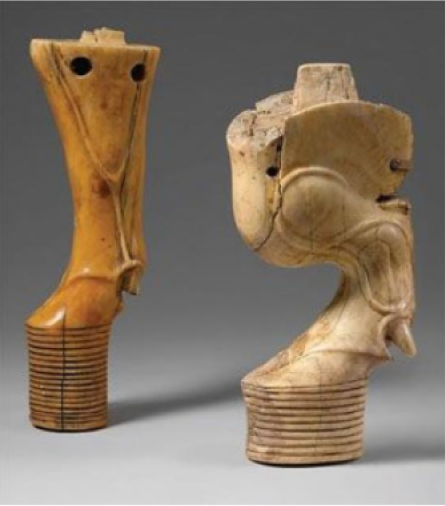
An iconic piece of furniture that dates back to Ancient Egypt is the throne, with intricate carvings and embellishments of stones and metals inlaid throughout the design.
Often, parts of the throne were designed in the shape of animal legs, representing the Pharaoh’s divine authority over the animal kingdom.


Acacia

Sycamore

Ebony
Eye-catching designs resulted from importing woods from other regions, with commonly used woods being acacia, sycamore, and ebony.
They used these types of wood to make other furniture, such as beds, which also had great cultural significance in the Ancient Egyptian period.
Ancient Egyptians Beds
Bed headboards were often designed with intricate carvings of gods and hieroglyphs, again with the legs of the bed representing animal legs.
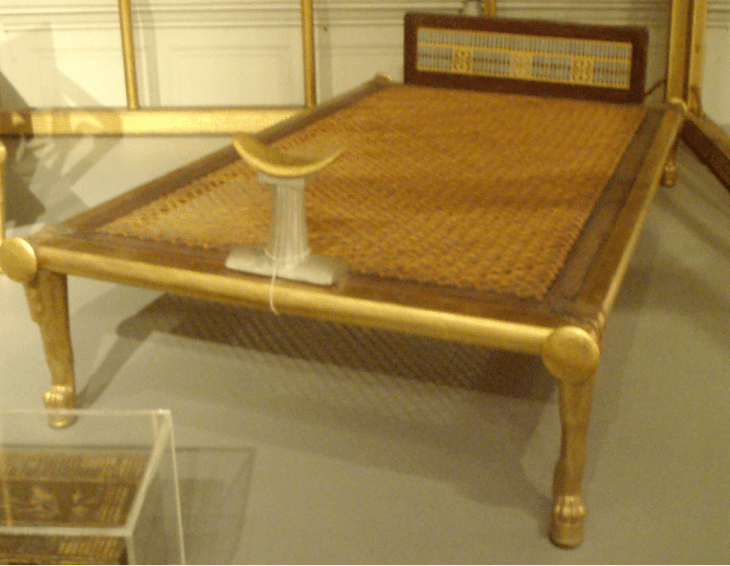

It’s believed that the bed symbolized the afterlife, so it was important for the Egyptians to convey this within their design.
From materials to design elements, Ancient Egyptian furniture was created for much more than practical purposes and instead represented wealth and class. Ancient Egyptian furniture showed clear signs of evolution, from intricate designs representing different parts of Egyptian society to more practically designed pieces that stood the test of time.
Greek Furniture
In contrast to Ancient Egyptian furniture, Greek furniture focused on practicality and brought functional pieces into living spaces. The primary materials used for crafting Greek furniture were wood and marble, with oak, maple, and cedar being the most common types of wood used.
Common types of furniture in ancient Greece were chairs and stools, which often consisted of wood and a woven seat.
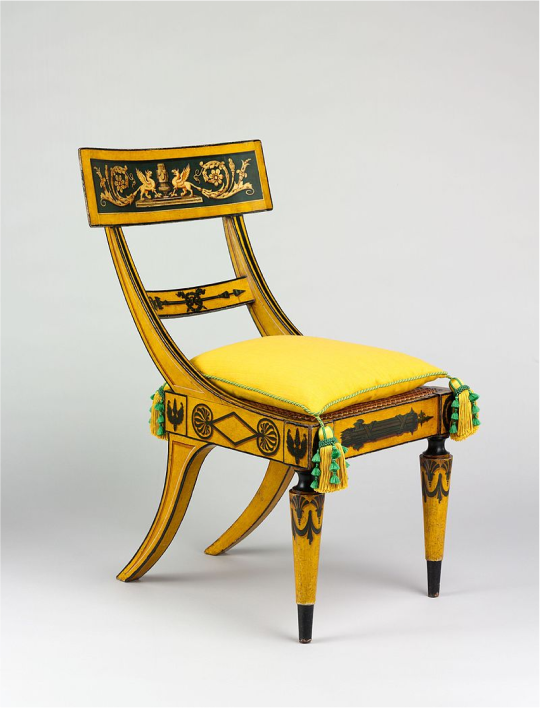


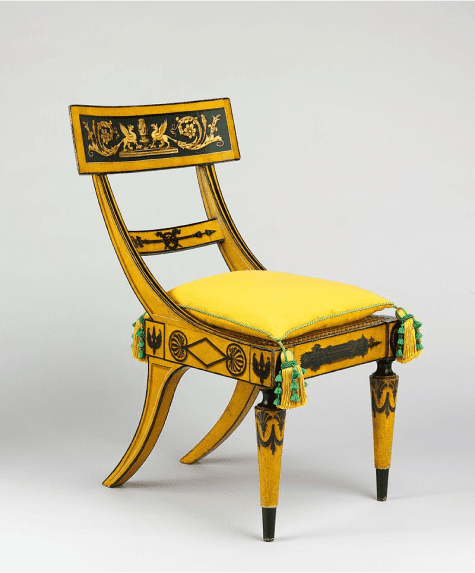
Klismos Chair
Greeks implement curved structures into their chair designs for added comfort, showing an evolution in how furniture was crafted to reflect human needs, no longer just offering basic support.
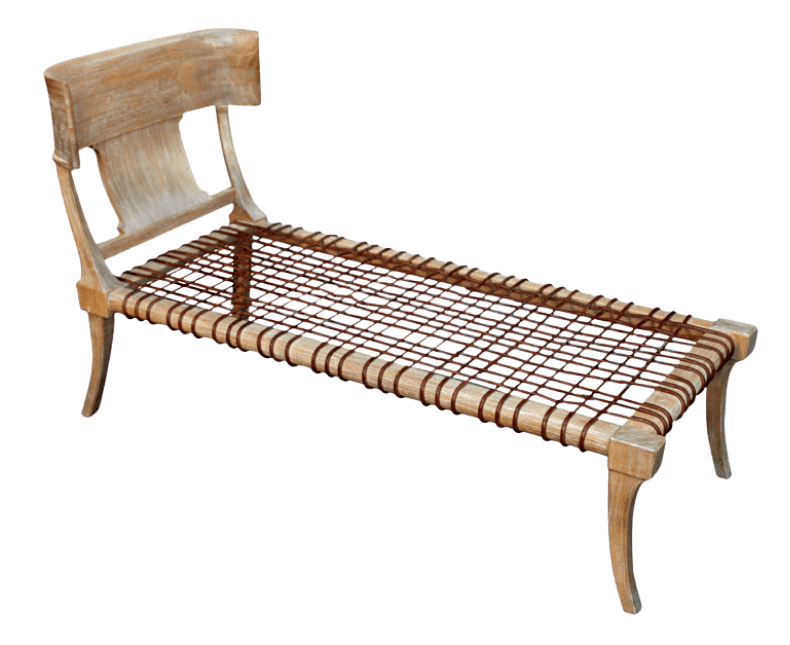

Klismos Bed
Tables became an integral part of dining, often made from wood in rectangular shapes that stood low and held the weight of essential items. Beds continued to be crucial pieces of furniture, designed with a simple rectangular wooden frame and woven ropes to provide mattress support.
While practicality was at the forefront of Ancient Greek furniture, often carvings and painted decorations were included in their designs to add extra visual interest.
Greeks saw furniture as a way to use natural materials and complement their living spaces, providing an ultimately simple but effective architectural style.
Roman Furniture
Ancient Roman furniture took much of its inspiration from the Ancient Greeks, but with slight differences that reflect Roman culture. Again, wood was the primary material used, with the three main types of maple, pine, and oak. For a decorative effect, Romans used bronze and marble.
Similarly to the Greeks, Romans designed stools out of wood with woven seats for added comfort.
Cleverly, the Romans created chairs called ‘Curules’ that could be folded and taken to officials, again honing in on furniture made for practical uses.
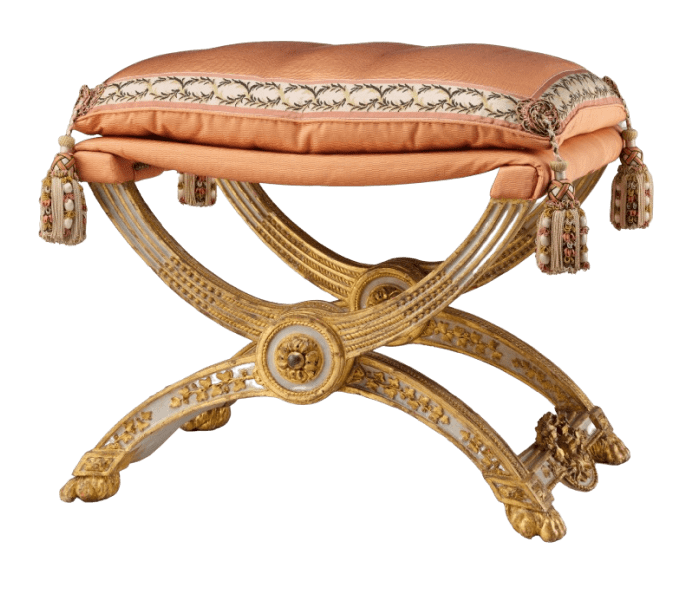

Curule Style, 1786
Tables and beds were also common pieces of furniture that included decorative elements in their designs. Romans often inlaid table tops with marble for aesthetic value while using fluted wooden legs to ensure the furniture served its purpose, similar to inlaying beds with ivory for the same reason.
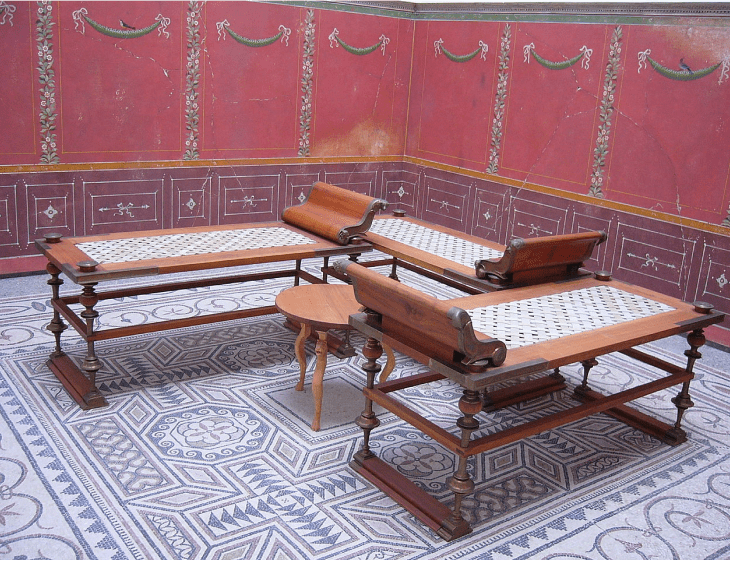

Triclinium
Ancient Roman furniture was big on comfort and style, with sofas being incorporated into social gatherings, designed from wood and woven or cushioned seats with sloping backrests for comfort.
With bronze, marble, and wood used to reflect the sophistication and wealth of the Roman Empire, Roman furniture was an influential period when considering furniture designs and evolution.
Furniture From
The 12th to 17th
Century

Gothic Furniture
How we think of Gothic interiors and styles of furniture in the modern era differs from how these styles initially looked. However, you’d be correct in assuming furniture from the Gothic period (12th-16th century) was elaborate, decorative, and intricate.
Primary materials used for Gothic furniture were wood,

Oak

Walnut
with oak and walnut being some of the most common. Pointed arches, intricate features, and geometric carvings were just a few of the leading visionary points of Gothic furniture.
Chairs, stools, and tables were common in Gothic furniture with similar designs in which religious symbols were carved into different parts of the furniture.
In both pieces, the legs often replicated animal legs to further implement a sense of grandeur. Beds also expressed a similar level of extravagance, with headboards and footboards used to replicate animal and human figures.
A furniture piece that grew in popularity throughout the Gothic period was chests and drawers, often symbolizing wealth because they were used to store valuables.
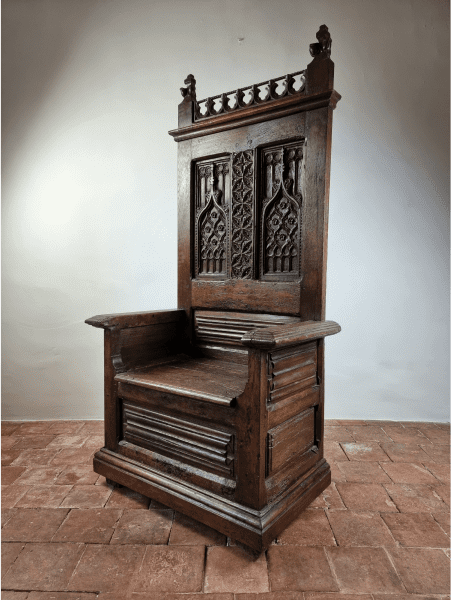

Overall, Gothic furniture was designed with the luxury of the Gothic period in mind, with intricate carvings representing cultural beliefs to large geometric designs that still stand out and continue to be popular with those interested in interior design.
Renaissance
Furniture
Renaissance furniture brought classic design motifs back to life, offering a more simplistic style than Gothic furniture. Emerging in the 15th century in Italy, this furniture style honored symmetry and balance and eventually grew in popularity across Europe in the 16th century.
Similarly to other types of furniture, the Renaissance period used woods such as walnut, mahogany, and oak to bring their creations to life. Intricate carvings of classical motifs were often included in designs, adding upholstery for chairs and stools in opulent satins and velvets.
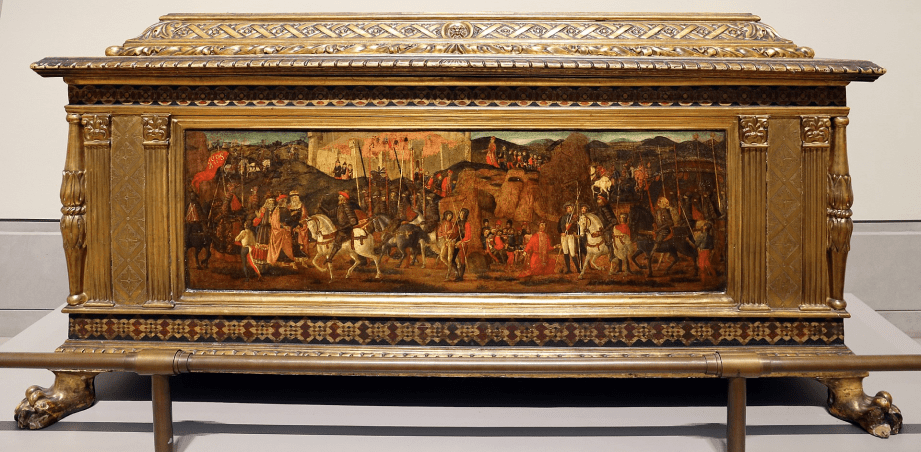

This period’s furniture included tables, cabinets, and beds, with different carvings and embellishments to add visual interest and excitement to their designs. Cabinets were a focal point for this, with ivory and mother-of-pearl representing wealth.
The Renaissance period was all about wealth and sophistication, and the furniture of this period was no different. Those with an eye for classic designs and intricate carvings sway toward Renaissance furniture, with its visual interest still relevant today.
Baroque Furniture
The Baroque era saw furniture become more dramatic and intricate, with emotions and movement explored in specific designs. Again, wood was the primary material used for each type of furniture, with mahogany, ebony, and walnut most commonly seen.
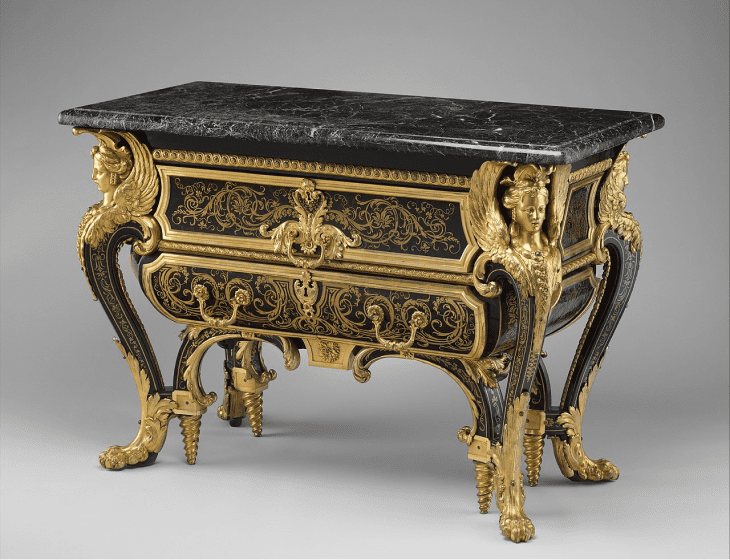

Cabinets were an item with fancy inlayings, such as ivory and tortoiseshell, used to store valuables representing status and wealth. The theatrical grandeur of Baroque furniture is still a popular choice for many.
Furniture in the
18th and 19th
Century

Age of
Enlightenment
From the late 17th to 18th century, the Age of Enlightenment saw furniture become more practical. This change went hand in hand with science and individualism, seeing society become more geared toward reason.
Ornamentation and decorative aspects were kept minimal, with symmetry, simplicity, and clean lines taking center stage to honor this functional furniture style.
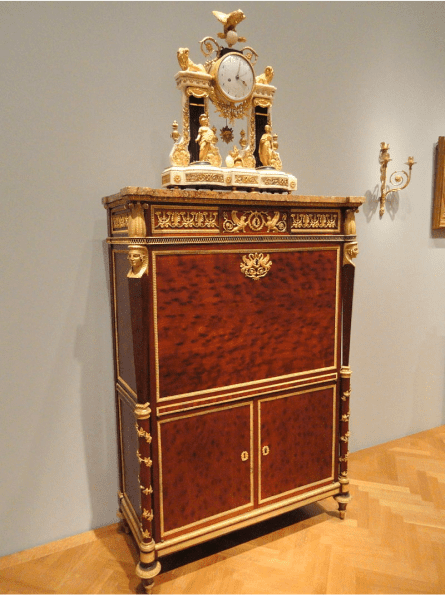

This development led to the design style known as Neoclassicism, which took much of its inspiration from Greek and Roman designs which we covered earlier in our article.
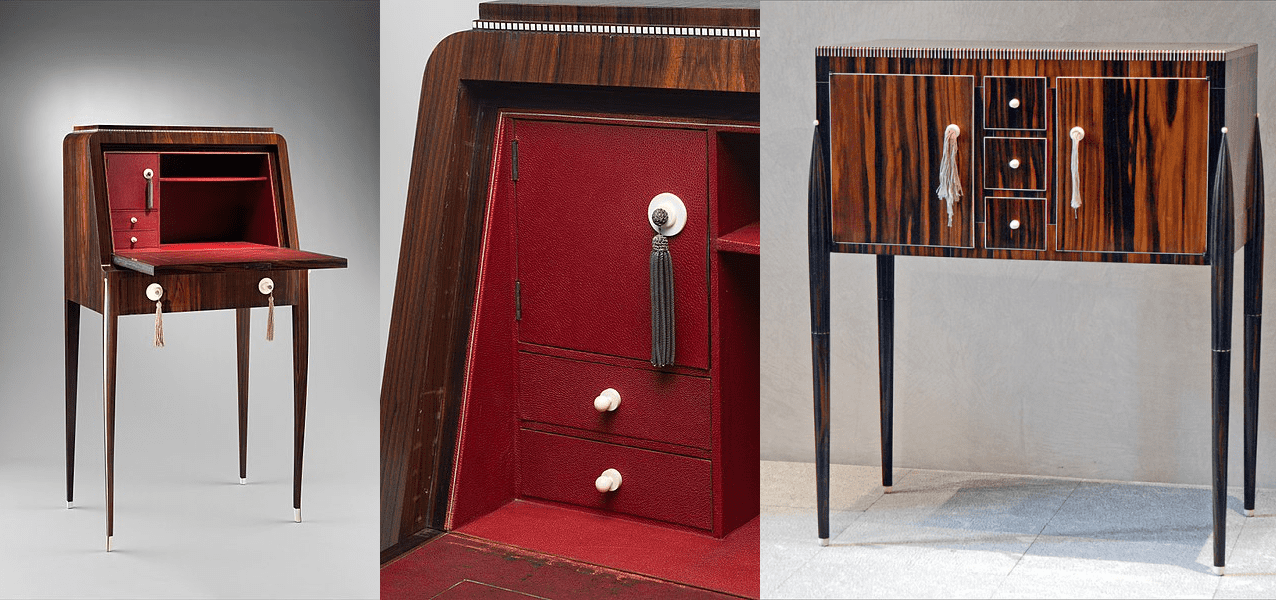
Secretaire
Cleveland Museum of Art
Going hand in hand with practical designs were functional, durable materials that could be manipulated into specific shapes with newly developed techniques such as steam bending, which created curved shapes that were both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
As society continued to evolve in this time, furniture designs and styles became more eclectic and reflected this change.
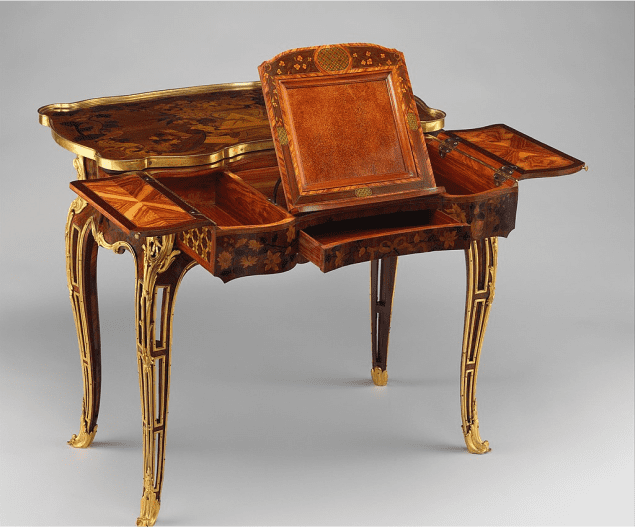

Mechanical writing table
Metropolitan Museum
Designs incorporated elements from various periods and cultures, which became renowned as the Roco style, seeing asymmetric and ornate decoration come to life.

Although this diverse style came into play, the Age of Enlightenment represented a time that furniture designers shifted from heavily ornamented designs and instead focussed on the functionality of their pieces, with contemporary designers still heavily influenced by this period.
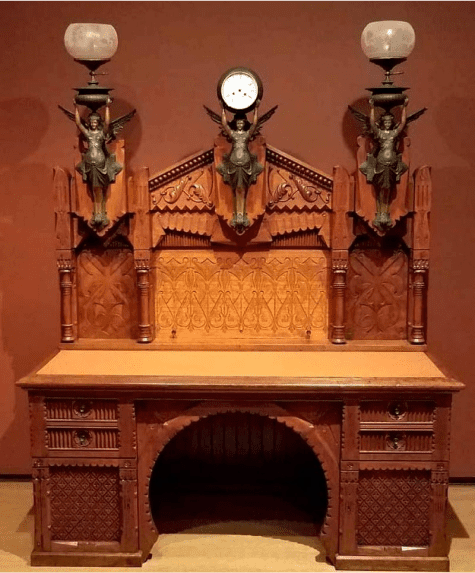
Victorian Era
The Victorian era spanned from 1837 to 1901 and saw furniture styles become more varied, with both heavily decorated and simplistic designs available. This era was defined by growth and prosperity in the United Kingdom.
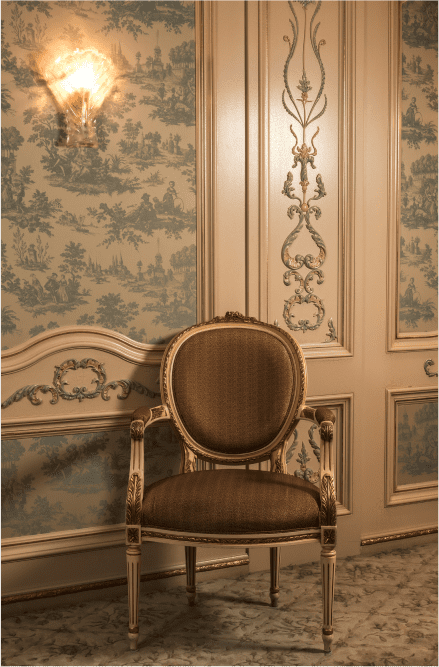

Victorian Chair
Nature often inspired motifs and ornamentations, with flowers, animals, and leaves commonly embellished on furnishing designs. This design was referred to as Neo-gothic and is incredibly distinctive for Queen Victoria’s reign.

As time passed, the Victorian era saw broader styles, in which many previous design styles were merged together to create the Victorian eclectic revival. Exoticized cultures were predominantly seen in these designs, with Egyptian design motifs being popular.
Materials used for furniture became more diverse, too.

Mahogany

Rosewood

Oak

Walnut
We saw the likes of mahogany, rosewood, oak, and walnut, commonly used for various items, all finished with pristine polishings that helped them stand out and look truly remarkable.
Arts and Crafts
Movement
Emerging in the 19th century, the Arts and Crafts movement developed to counteract the Industrial Revolution’s mass production of machine-made goods.
Poet, designer, and social activist William Morris
was a leading figure in this movement and believed that the cheap, low-quality goods produced at this time negatively impacted the quality of life, leading him to advocate for returning to traditional craftsmanship and design methods.
Morris created the Morris Marshall, Faulker & Co. Company in 1861 (later known as Morris & Co.), producing handcrafted furnishings that honed in on high-quality and more artistic approaches to decorative objects.

Going hand in hand with Morris’ art was his social activism, in which he fought for the rights of artisans to improve their working conditions and wages in the hope that this vocation would become more respected and valued.

Morris and Company Textile
Printing Merton Abbey
His activism led to the development of the British Labour Party, a political party with workers’ rights and liberal views at its core.
Art-wise, Morris’ impact is still renowned today, inspiring artisans to incorporate traditional techniques into their artwork in a world continuously evolving with access to machinery and modern manufacturing techniques.
20th Century
Furniture

Art Nouveau
Drawing inspiration from nature’s flowing lines and shapes, such as flowers, leaves, and vines, and using new materials, such as curved glass and wrought iron, led to the Art Nouveau period.
This era revolved around innovation and modern techniques featuring asymmetrical shapes. Laminated wood and bentwood grew popular, seeing designers become more experimental with techniques such as steam bending to create modern curved shapes.

Bahut art nouveau
(La Berce des prés) (“Hogweed”)
French artist, Emile Gallé,
was one of the most influential artists of the Art Nouveau era, becoming well known for his experimentation with glass and creating designs with delicate shapes and intricate inlaid designs.

The Art Nouveau movement stepped away from traditional techniques and focused on artistic evolution and experimentation with new materials and modern designs.
Art and furniture from this era are still highly regarded by designers and collectors and are pivotal moments in furniture making.
Art Deco
Art Deco has distinctive characteristics such as geometric shapes, luxurious materials, and bold colors. This infamous style started in the 1920s, growing in popularity through the 30s as the modernist movement took center stage, drifting away from intricate, delicate features common in eras such as Art Nouveau.
Unlike many other design eras, Art Deco centered around symmetry, with geometric shapes such as trapezoids and chevrons accompanying traditional circles.

Art Deco was a style that oozed luxury, with opulent materials such as marble, exotic woods, and metal in vibrant shades of chrome and silver commonly used. These materials added to the high-quality feel of art deco furniture, with sleek designs that added to the modern aesthetic.
Corner cabinet
of Mahogany
This era wasn’t only about the artistic value, as designs became more functional due to access to machinery, which saw designers combine industrial motifs in their work. Practical features included the likes of hidden drawers and wheels.

There were many influential Art Deco designers, such as Jules Leleu and Jean Dunand, but one of the most prominent figures was Jacques-Emile Ruhlmaan, who was mainly well-known for using exotic woods.
Ruhlmann (centre)
with his team of designers at 27 rue de Lisbonne in Paris
Furniture pieces
designed by Jacques-Émile Ruhlmann
Contemporary furniture styles still incorporate Art Deco features, with vintage Art Deco designs being highly sought after by collectors. The Art Deco movement was a poignant moment in the design world, seeing social change continue to be reflected in art pieces.

Bauhaus
At the center of the Bauhaus movement was the Bauhaus School, founded by Walter Gropius in 1919, which saw designs increase in practicality while incorporating a minimalist, simple modern flair.
Industrial productions were widely embraced during this movement, with materials such as tubular steel, plywood, and glass able to be efficiently manufactured into aesthetically pleasing shapes that suited a wide range of consumers.
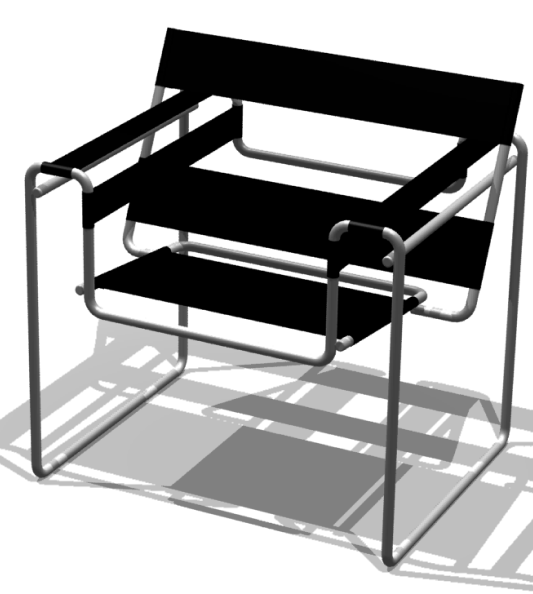
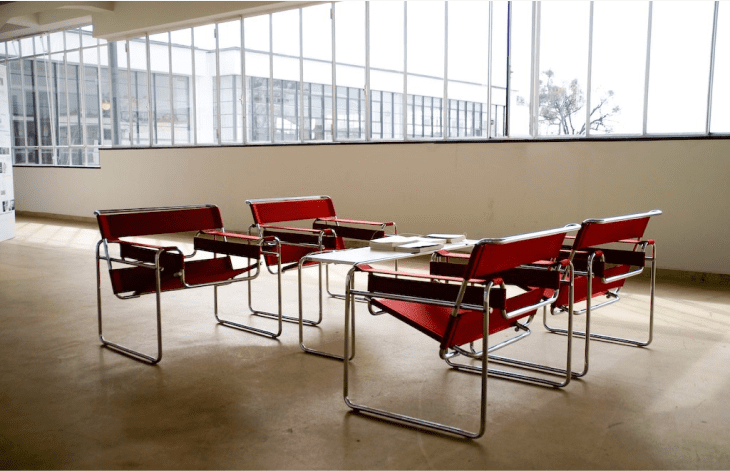
Wassily chair
Marcel Breuer was a crucial figure in Bauhaus furniture,
with his Wassily chair remaining incredibly influential due to its innovative design. His chair was created in 1925 and featured a simplistic design consisting of a tubular steel frame with a leather seat and back.
Of course, other influential Bauhaus designers, such as Ludwig Mies van der Rohe and Mart Stam, were known for their iconic designs like Rohe’s Barcelona Chair and Stam’s tubular steel cantilever chair.

Similarly to Art Deco furniture,
Bauhaus often used distinctive geometric shapes and clean lines for an eye-catching effect, paired with bold colors and clashing materials such as leather and metal.

These characteristics may sound impractical, but they didn’t alter the functionality of Bauhaus furniture, ensuring final designs were aesthetically pleasing and practical.
We can thank the Bauhaus era for steering furniture toward becoming more practical while keeping sight of the artistic joy that innovation can bring with modern manufacturing techniques and new materials, ensuring functionality was excitingly brought to life.
Mid-Century
Modern
Coming to fruition in the 1940s to 60s, Mid-Century Modern furniture was centered around simplicity and minimalism, with clean lines and natural materials commonly used. This step down to simpler styles reflected the needs of post-war society, in which practicality was a priority.
Bauhaus acted as a primary inspiration for Mid-Century Modern furniture, with designers striving to include aesthetically pleasing elements while prioritizing functionality.
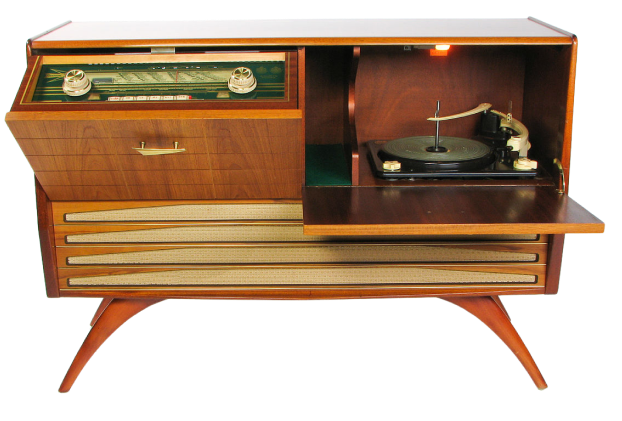

Teak and hardwoods grew in popularity because they look natural with minimal treatment, further accentuating the natural feel of this era.
Another priority for Mid-Century Modern furniture designers was ergonomics, in which creations were made to reflect ease of use and efficiency. Items like chairs featured low-slung designs for comfort, with leather and vinyl surfaces requiring minimal maintenance and maximum durability.
Charles and Ray Eames are some of the most well-known designers from this era, with their Ottoman and Lounge Chair renowned as some of the most iconic designs of the time.


Much Mid-Century Modern furniture is still sought after by collectors and designers alike, favored for its functionality and simple structures.
Postmodernism
Postmodernism rejected the notion of following function, presenting a rebellious style that prioritized art. Designers took inspiration from many sources to create visually striking pieces, proving that modernist manufacturing techniques and ideas weren’t the only way to make high-quality furniture.
Asymmetric shapes once again became more popular in this furniture style, with designers becoming increasingly experimental with form and structure to create remarkably eye-catching pieces.
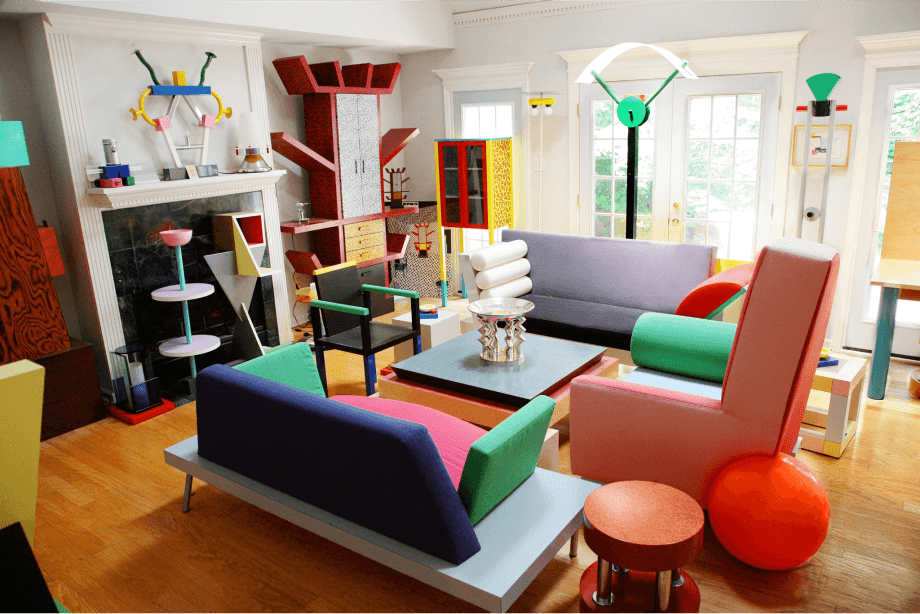

This redirection of art and furniture saw many creative minds join together, including Memphis Group, a collective founded in Italy during the 1980s. These styles were bold and intriguing, a far way from the likes of Bauhaus and Mid-Century Modern.
Postmodernism was a pivotal design era and is still hugely influential in interior design, inspiring designers and collectors to push boundaries and see that furniture doesn’t only need to be created in one practical way and can instead focus on art.
Common Materials
and Techniques
Through Time

Our furniture timeline indicates that multiple materials remained popular choices throughout different periods. Let’s take a look at these materials and the techniques needed to make them perfect for furniture;
Wood
Wood dates back to prehistoric times, with ancient civilizations being the first to use it for furniture due to its strength, durability, and resilience. As manufacturing techniques have evolved over the past few centuries, our understanding of wood has deepened. Designers now have specific strategies to honor its beauty through shaping, joining, and finishing.
Accompanying the development of manufacturing techniques is our access to different types of wood.
Of course, from here,
Manufacturing techniques and the types of wood available continued to evolve, with wood still being one of the most popular furniture materials.
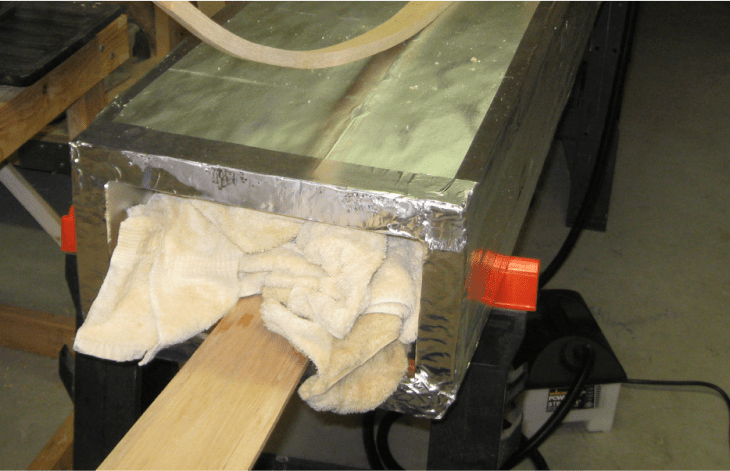

Steam bending and lamination were popular techniques that allowed the wood to become more versatile and bend into different shapes to reflect practicality and style simultaneously. Traditional handcrafted methods are popular in bespoke industries that favor uniqueness.
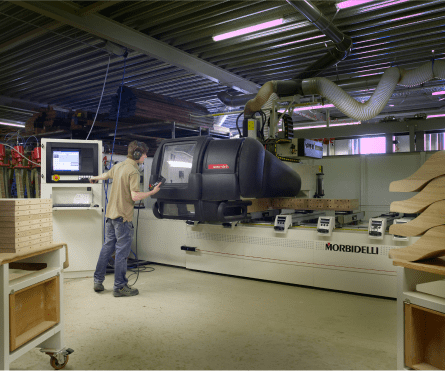
CNC machine
In the 21st century, we are fortunate to have access to remarkably advanced technologies, such as CNC machining techniques, which allow designers to push boundaries and explore the properties that wood offers.
Metal
Metal is an exciting furniture component, and it started as a way of adding decorative elements and small functional features such as hinges. As centuries have passed, metalworking techniques have evolved and continued to grow to help designers find different ways to include types of metal in furniture designs.
For example,
The Middle Ages saw functionality grow, with metalworkers creating frames and support for tables and chairs. At the same time, the likes of brass studs and iron hinges were added for decorative effect.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution saw further advances regarding metal, with cast iron able to be used for outdoor furniture, providing designers with other opportunities. This development went hand in hand with the Art Nouveau movement, which saw metalwork used more artistically for intricate details and flowing lines.

The Modernist movement saw metals rise in popularity for furniture designers, with the likes of Marcel Breuer using steel, chrome, aluminum, and other metals to optimize the sleekness of their designs. Of course, there’s also the iconic work of the Bauhaus School, in which tubular steel was used.
Although metal isn’t the most essential material regarding furniture, it has proven on several occasions to have its purpose and continues to be used for decorative components and practical features such as handles.
Glass
Egyptians and Romans were some of the first known civilizations to use glass for furniture, using the material to add decorative elements to various types of furniture. As time passed, glass use became more popular and outgrew the restraints of just being used for decorative purposes.
Using glass in furniture has continued to evolve since this time, with modern designers incorporating various techniques and types of glass in their furniture. For example, laminated and tempered glass are popular in durable and large pieces, with frosted and colored glass used for artistic value on contemporary designs.
Plastic
Plastic in furniture is a more recent addition, only developing in the last 100 years. Celluloid was the first plastic to be invented back in the 1860s, but it took around another fifty years for plastics to be developed to a suitable standard that could be used for furniture.
The 1930s saw the first plastic chairs created from Bakelite. This thermosetting plastic can be molded into various shapes and colors, making it the perfect material for various types of furniture.

During World War II, plastic production began to surpass the quality of Bakelite as plastics such as polyethylene and polystyrene were developed.
These newly developed plastics were highly regarded because of their flexibility, leading to lighter, more versatile furniture pieces.


Verner Panton
The 60s and 70s saw plastic become a more integral element of furniture design, with various designers (Joe Colombo and Verner Panton, for example) creating exceptionally innovative designs that celebrated the flexibility of this material through bright colors and unique shapes.
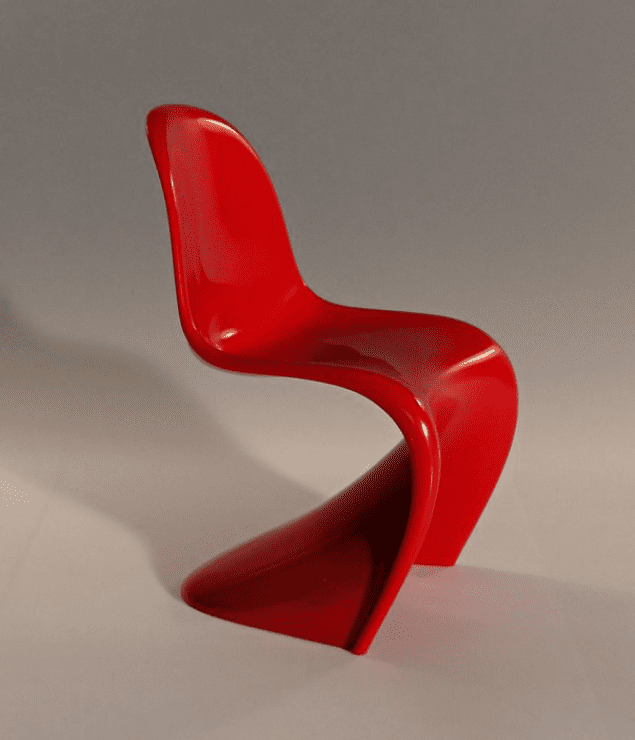

Plastic has always stayed in style and is still a massive feature of today’s furniture industry. With innovative manufacturing and production techniques such as 3D printing and injection molding enabling designers to get even more creative, we can safely assume that plastic will remain popular. However, environmental issues come with plastic, creating a need for recycled plastics and alternatives.
Upholstery
Upholstery is another furniture craft that has been around for centuries. Ancient civilizations upholstered chairs and stools with woven textiles and leather to elevate their comfort and improve their functionality.
Upholstering furniture grew in popularity throughout the Middle Ages, with European designers covering beds and chairs in fabric that was often elaborately decorated with tassels and embroidery.
The love for upholstery flourished in the Renaissance, with furniture makers stuffing their creations for added comfort and intricate eye-catching designs.
Armchair (1788)
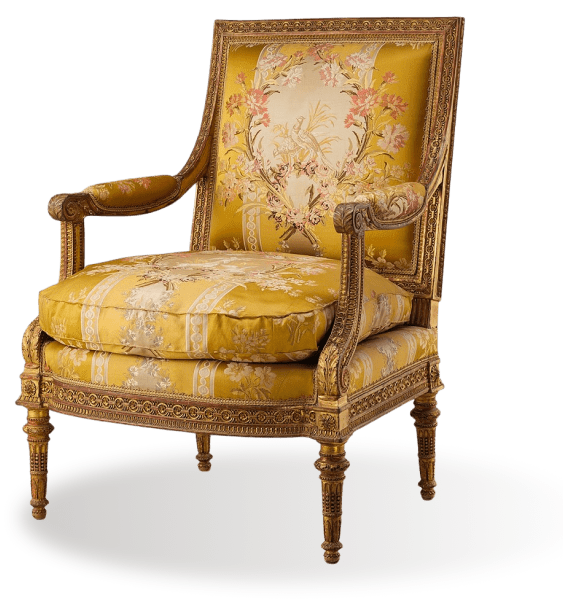


As techniques and materials became more accessible, upholstering became integral to furniture design during the 18th and 19th centuries. With new fabrics, broader color ranges, springs, and other materials available, designers could get more inventive, leading to upholstering becoming almost a separate art form.
As we entered the 20th century, upholstery continued to evolve. Synthetic materials were introduced, which led to a more durable and long-lasting approach, along with vinyl and leatherette, which made for contemporary additions.
Furniture and
Culture

Furniture and
Social Status
During our timeline, it’s clear that furniture has much more value than the fact it’s functional and can even play an essential role in society and religion. Connotation of furniture quality and wealth date back to Ancient Egypt and evolved into the 19th century, with luxurious materials such as silk indicating wealth. Of course, this mindset is still apparent today, with high-end furniture seen in more exclusive locations.

We can apply this mindset to the level of elaboration specific furniture pieces have. For example, in the Middle Ages, those higher up in society would have thrones, whereas lower-class individuals would use benches and items that were much less elaborate.

Again,
This contrast between practical items with little ornamentation and extravagant items has stayed with us in society, with royals still using opulent thrones and furniture.
Furniture and
Religious Practices
Religious churches are still equipped with furniture to give worshippers all they need to pursue practices. Traditional furniture pieces, such as alters, date back centuries, complete with intricate carvings and religious figures.
Different periods, such as Ancient Egypt, can be thanked for getting us to where we are today.
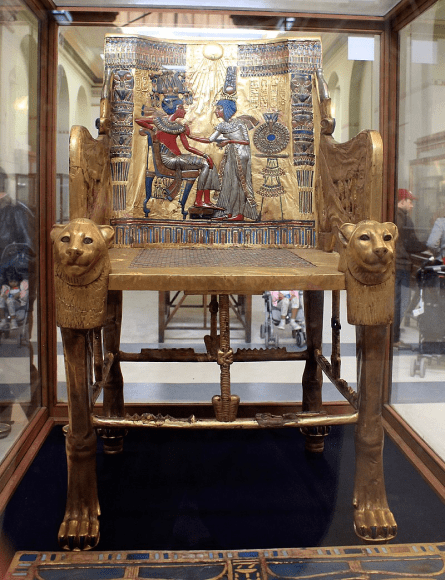

The Egyptian
The Egyptians used furniture during worship, with chairs and tables to hold religious items and provide seats for worshippers. Other religions, such as Christianity, continued this with elaborate ornamentation to convey faith.
Furniture and Art
Furniture is an art form in itself, and we see historical pieces of furniture from the 20th century and earlier presented in museums worldwide to indicate various periods.
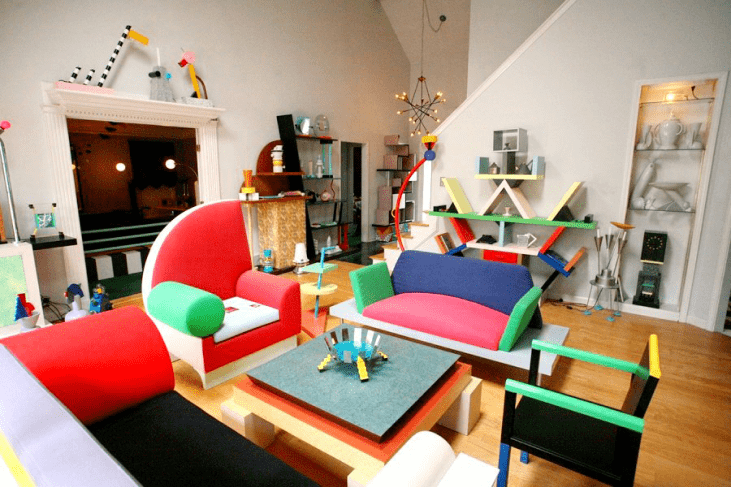

As technology continues to evolve, designers and artisans are becoming increasingly experimental, ensuring furniture is an art form that will be preserved.
Conclusion

Throughout centuries of development and evolution, furniture design has continually expanded to make it what it is today. From gaining access to more materials to understanding how specific manufacturing techniques can achieve certain results, designers have come a long way, and contemporary design reflects both practicality and art.
What is the history of wood furniture?
Wood furniture has a long history, dating back thousands of years. It was used in ancient times, seen in Egyptian tombs and civilizations like China and Greece. In the Middle Ages, European craftsmen created detailed designs and carvings. Over time, different styles emerged, like the opulence of the Renaissance and the simplicity of the Industrial Revolution. Today, wood furniture remains popular, made using a blend of traditional and modern methods.
What is the history of furniture as art?
Furniture has a long history as art, dating back to ancient civilizations where it represented wealth and status. In ancient Egypt, furniture was made from precious materials and intricately carved.
During the Renaissance, furniture became more ornate and decorative, with intricate carvings and gilding. It was seen as art, with craftsmen and artists creating functional yet visually stunning pieces.
Furniture design changed in the 20th century with the Modernist movement. Designers like Le Corbusier and Charles Eames focused on simplicity, functionality, and minimalism, challenging traditional ideas of furniture as purely decorative.
Furniture is still an art form, with designers always trying new things.
Where was the first furniture made?
The first furniture was made in ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China. These early civilizations developed the skills and techniques necessary to create basic furniture using materials such as wood, stone, and animal skins.
What is the oldest furniture in the world?
The oldest furniture in the world is believed to be the pieces found in the tombs of ancient Egyptian pharaohs. These furniture pieces date back to around 3100 BC and include beds, chairs, tables, and chests.
What is the importance of furniture?
Furniture is important because it provides functionality, comfort, and aesthetic appeal. It enhances the overall functionality and organization of a space. Furniture allows us to store and display items, sit or lie down, and perform activities efficiently. It also adds style and personality, contributing to the room’s ambiance and visual appeal. Without furniture, our living and working spaces would lack comfort and functionality.
Who created modern furniture?
Modern furniture was created by a combination of designers, architects, and furniture manufacturers who sought to break away from traditional styles and create innovative and functional pieces. Some notable figures in the development of modern furniture include Le Corbusier, Charles and Ray Eames, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, and Marcel Breuer. These individuals and many others played significant roles in shaping the design principles and aesthetics of modern furniture.
What was old furniture made of?
Old furniture was typically made of wood, such as oak, mahogany, or walnut. However, depending on the period and region, other materials such as metal, stone, or even animal bones could also be used in the construction of furniture.
What was the first furniture invented?
The first furniture invented is believed to be the simple wooden stools and benches, which were used for sitting and resting. These basic forms of furniture date back to ancient civilizations and were essential for providing comfort and support in early human settlements.